一些认识
图的广度优先搜索可以看作是树的先序遍历,先处理当前节点,然后将当前节点的状态加到总的状态中,再传递给后序的节点。
图的深度优先搜索可以看作是树的后序遍历,先处理子节点,当遍历完所有的子节点以后,再根据子节点的返回值判断当前应该做的事情。
深度优先DFS+回溯
Leetcode-216. 组合总和 III
难度:⭐⭐
自己完成程度:稍微花了一点时间完成
本题不难,我分别实现了广度优先搜索和深度优先搜索两种方法
【BFS】:
class Solution {
private:
vector<vector<int>> res;
public:
void bfs(int be, int end, int k, int n, int len, vector<int> path){
for(int i = be; i <= end; i++){
vector<int> newPath = path;
int l = i + len;
if(l == n && (int)newPath.size() == k-1) {
newPath.push_back(i);
res.push_back(newPath);
}
else if(l < n && (int)newPath.size() < k-1){
newPath.push_back(i);
bfs(i+1, end, k, n, len+i, newPath);
}
}
}
vector<vector<int>> combinationSum3(int k, int n) {
vector<int> path;
bfs(1, 9, k, n, 0, path);
return res;
}
};
我认为BFS比起DFS更加直观一些,因为它不存在回溯,只需要想好当前问题的子问题的初始条件,就可以递归下去。它的问题也很明显,像这种需要记录所经过路径的问题,BFS每到一个新的分支,就需要将当前的结果复制一下传到下一层,时间和空间的花费较高。
【DFS】:
class Solution{
private:
vector<vector<int>> res;
const int Begin = 1;
const int End = 9;
public:
void dfs(int be, int sum, int k, int n, vector<int>& path){
for(int i = be; i <= End; i++){
path.push_back(i);
if(sum + i < n && path.size() < k) dfs(i+1, sum+i, k, n, path);
if(sum + i == n && path.size() == k) res.push_back(path);
path.pop_back();
}
}
vector<vector<int>> combinationSum3(int k, int n) {
vector<int> path;
dfs(Begin, 0, k, n, path);
return res;
}
};
DFS如果能够想清楚的话,思路也是较为简洁的。DFS的思路便是,先沿着一条路径遍历下去,直到这个路径遍历完,或者找到了一个解,然后再返回上一分支,再开始下一次遍历。
这里在dfs一开始,就先将下一分支的情况加入到路径中。假如这一分支暂时符合要求,就让它继续做dfs;如果这一分支不符合要求,就再将其从路径中弹出;如果这一分支恰好就是问题的解,就将当前的路径结果保存,并将当前分支弹出。
这里dfs的参数是 &path,也就是说,只需要在初始状态申请这样的一个path vector,就可以在遍历和回溯的过程中一直使用。极大地缩减了空间复杂度。
本身函数的递归就是不断压栈和出栈的过程,这里使用&path刚好借助了函数的压栈出栈实现了回溯。
Leetcode-131. 分割回文串
【1】这个题,一上来我用的暴力递归来做的,代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
bool is_palindromic(string s, int start, int end){
for(int i = 0; i < (end - start + 1) / 2; i++){
if(s[start+i] != s[end-i]) return false;
}
return true;
}
vector<vector<string>> partition(string s) {
vector<vector<string>> ans;
if(s.size() == 0){
vector<string> temp;
ans.push_back(temp);
return ans;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= (int) s.size(); i++){
if(is_palindromic(s, 0, i-1)){
vector<vector<string>> temp = partition(s.substr(i));
for(auto t : temp){
vector<string> temptemp;
// cout << s.substr(0, i) << endl;
temptemp.push_back(s.substr(0, i));
for(auto str : t)
temptemp.push_back(str);
ans.push_back(temptemp);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};
【2】看了题解,才想到使用深度优先递归加回溯来做。好久没做递归+回溯了,都有点生疏了:
class Solution {
private:
vector<vector<string>> ans;
public:
// 判断是否是回文
bool is_palindromic(string &s, int start, int end){
for(int i = 0; i < (end - start + 1) / 2; i++){
if(s[start+i] != s[end-i]) return false;
}
return true;
}
void func(string &s, int start, int end, vector<string> &temp){
if(is_palindromic(s, start, end)){
string substr = s.substr(start, end-start+1);
temp.push_back(substr);
if(end + 1 == s.size()) // 说明到了字符串末尾
ans.push_back(temp);
else
for(int i = end + 1; i < s.size(); i++)
func(s, end+1, i, temp);
temp.pop_back();
}
}
vector<vector<string>> partition(string s) {
vector<string> temp;
if(s.size() == 0)
ans.push_back(temp);
else
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
func(s, 0, i, temp);
return ans;
}
};
【3】想到可能会有一些重复计算的字符段,如果计算过便保存下来,可能会快一些。于是设计了一个双层哈希来存储,结果效果并不明显。可能重复计算带来时间复杂度的增加,不简简单单是某一种情况的重复计算,而是虽然情况不同,但是所含区域的重复计算。所以这个问题解决了,也并没有带来时间复杂度的提升。
【4】看到题解里有,先利用动态规划,计算得到所有的回文串,也可以降低时间复杂度。
补充题目:
递归求解不同的二叉搜索树
Leetcode-95.不同的二叉搜索树
本题一直没做出来,看了答案才会做,其实直接用暴力递归就可以了,因为题目中也说了,n最大不超过8。
class Solution {
public:
vector<TreeNode*> func(int begin, int end){
vector<TreeNode*> res;
if(begin > end) {
res.push_back(nullptr);
return res;
}
for(int i = begin; i <= end; i++){
vector<TreeNode*> ltree, rtree;
ltree = func(begin, i-1);
rtree = func(i+1, end);
for(auto l : ltree){
for(auto r : rtree){
TreeNode* temp = new TreeNode(i);
temp->left = l;
temp->right = r;
res.push_back(temp);
}
}
}
return res;
}
vector<TreeNode*> generateTrees(int n) {
if(n == 0){
vector<TreeNode*> res;
return res;
}
return func(1, n);
}
};
/*
之前一直不想直接递归,想着做一下遍历+回溯,但是一直没有思路
看了官方题解,还是直接用递归来做。
*/
广度优先搜索
Leetcode-130. 被围绕的区域
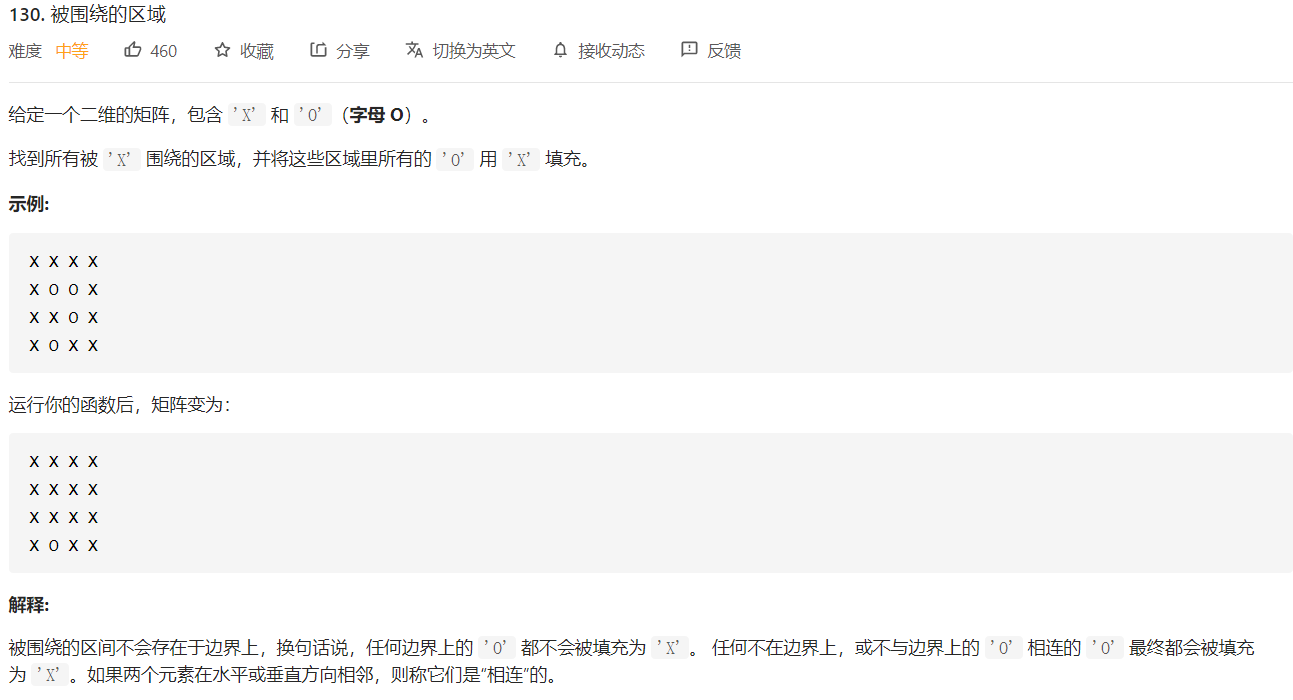
本题最初我的思路是,将这个问题看成是矩阵的一圈一圈的遍历过程,知道了外层的情况以后,从而确定内层有哪些O与外层的O相连。但是发现问题是更新不同步的问题。于是看了一下提示改用广度优先搜索的方法,利用队列实现。
struct Point{
int x;
int y;
};
class Solution {
public:
void solve(vector<vector<char>>& board) {
int rows = board.size();
if(rows == 0) return;
int cols = board[0].size();
queue<Point> q;
for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++){
if(board[i][0] == 'O') {
board[i][0] = '1';
q.push({i, 0});
}
if(cols-1 > 0 && board[i][cols-1] == 'O'){
board[i][cols-1] = '1';
q.push({i, cols-1});
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < cols; i++){
if(board[0][i] == 'O'){
board[0][i] = '1';
q.push({0, i});
}
if(rows-1 > 0 && board[rows-1][i] == 'O'){
board[rows-1][i] = '1';
q.push({rows-1, i});
}
}
// 开始广度优先遍历
while(!q.empty()){
Point p = q.front();
q.pop();
// 上
if(p.x >= 1 && board[p.x-1][p.y] == 'O'){
board[p.x-1][p.y] = '1';
q.push({p.x-1, p.y});
}
// 下
if(p.x + 1< rows && board[p.x+1][p.y] == 'O'){
board[p.x+1][p.y] = '1';
q.push({p.x+1, p.y});
}
// 左
if(p.y >= 1 && board[p.x][p.y-1] == 'O'){
board[p.x][p.y-1] = '1';
q.push({p.x, p.y-1});
}
// 右
if(p.y + 1 < cols && board[p.x][p.y+1] == 'O'){
board[p.x][p.y+1] = '1';
q.push({p.x, p.y+1});
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++){
if(board[i][j] == 'O') board[i][j] = 'X';
else if(board[i][j] == '1') board[i][j] = 'O';
}
}
}
};
Dijkstra算法
Leetcode-743. 网络延迟时间
假设一个图中有n个节点和m条边,则使用dijstra算法解决单源最短路径问题的时间复杂度是 $O(n^2)$,如果使用堆进行优化,则需要的时间复杂度是$O(mlogm)$。下面使用的是堆优化的dijkstra算法。
class Solution {
private:
struct my_greater{
bool operator()(const pair<int, int> &a, const pair<int, int> &b){
return a.second > b.second;
}
};
public:
int networkDelayTime(vector<vector<int>>& times, int n, int k) {
// pair.first 目标点的编号
// pair.seconde 该边上的传递时间
vector<vector<pair<int,int>>> edges(n+1, vector<pair<int,int>>());
for(auto t : times){
edges[t[0]].push_back(make_pair(t[1], t[2]));
}
// 计算迪杰斯特拉最短路径
vector<int> diji (n+1, INT_MAX);
vector<bool> visited (n+1, false); // 记录是否访问过,防止回头
diji[0] = INT_MIN;
int count = 0;
// pair.first: 节点编号(从1开始
// pair.seconde: 距离
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, my_greater> pq;
pq.push(make_pair(k, 0));
while(count < n && !pq.empty()){
pair<int, int> p = pq.top();
pq.pop();
int node = p.first;
if(p.second == INT_MAX) break;
if(!visited[node]){
visited[node] = true;
diji[node] = p.second;
count++;
vector<pair<int, int>> sub_edges = edges[node];
for(auto e : sub_edges){
if(!visited[e.first]){
pq.push(make_pair(e.first, e.second + p.second));
}
}
}
}
int ans = INT_MIN;
for(int d : diji){
if(d > ans) ans = d;
}
if(ans == INT_MAX) return -1;
else return ans;
}
};
拓扑排序
Leetcode-207. 课程表
本题做法就是拓扑排序,每次找到当前入度为0的点,并将其从图上移除,直到没有入度为0的点。
具体实现可以采用栈或者队列,用栈便是深度优先,用队列则是广度优先。
class Solution {
public:
bool canFinish(int numCourses, vector<vector<int>>& prerequisites) {
vector<vector<int>> nextCourse (numCourses, vector<int>());
vector<unordered_set<int>> aheadCourse (numCourses, unordered_set<int>());
for(auto p : prerequisites){
int n1 = p[0], n2 = p[1];
nextCourse[n2].push_back(n1);
aheadCourse[n1].insert(n2);
}
int ct = 0;
queue<int> q;
for(int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++){
if(aheadCourse[i].size() == 0){
q.push(i);
}
}
while(q.size() > 0){
int node = q.front();
q.pop();
ct++;
for(int next_node : nextCourse[node]){
auto ite = aheadCourse[next_node].find(node);
aheadCourse[next_node].erase(ite);
if(aheadCourse[next_node].size() == 0) q.push(next_node);
}
}
return ct == numCourses;
}
};
Leetcode-210. 课程表 II
二叉平衡树
1382. 将二叉搜索树变平衡
解法太巧妙。一般的解法都是O(n)的时间复杂度和O(n)的空间复杂度。而下面将一个二叉搜索树转换成平衡二叉树,有一种时间复杂度O(n)空间复杂度O(1)的方法。我解释一下这位作者下面代码的思路:
首先,它先把二叉搜索树转换成一个所有节点左子树都为空的斜向下的链,就像是一个链表。
然后每次将当前的一半的节点 n/2 个放到根节点的左子树上,取一个作为根节点,剩下的 n-n/2-1 个放到右子树上。这样不断划分,直到,当前这一堆中没有节点了,就返回一个nullptr。当左右两边都返回nullptr的时候,就得到一个叶子节点,该节点恰好就是整个树的最左节点,记为L,也就是刚刚的链表的头节点。这个时候要注意,这里的nextRoot是一个指针引用,就在将右子树设置为空的时候,传入右子树的是一个head=nextRoot->right,进入右子树以后,nextRoot=head,也就相当于每当右子树为空,就nextRoot沿着链表往下移一个位置,则这个节点刚好落在刚刚的L上面,成了L的parent节点,记为A。此时A的右子树也是同样,如果右子树分到了1个节点B,那B的右子树为空,也会返回一个B->right,作为返回值,记为C,此时C也恰好是整个以A为root的子树的下一个节点。还记得之前每次平均分成两堆,所以不会出现不平衡的情况。后面的过程依次类推。
// 先转换为最坏情况的二叉搜索树,即所有节点都只有右孩子,可以看作一条斜向下的链表,然后递归的转换为平衡二叉树
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* balanceBST(TreeNode* root) {
TreeNode* head = new TreeNode(-1);
TreeNode* tail = head;
int n = inorderVisit(root, tail);
tail = NULL;
return turn(head->right, tail, n);
}
int inorderVisit(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* &last){ //将二叉搜索树变为最坏情况,所有节点都只有右孩子,顺便计算节点数
int l = 0, r = 0;
if(root->left)
l = inorderVisit(root->left, last);
last->right = root;
last = root;
if(root->right)
r = inorderVisit(root->right, last);
return l+r+1;
}
TreeNode* turn(TreeNode* head, TreeNode* &nextRoot, int n){ //每次将中间的节点作为根节点,将左右子树转为平衡二叉树,n为当前子树节点数
if(n == 0){ //用一个指针引用nextRoot在转平衡二叉树的同时记录下一个作为根节点的节点,这样不用每次都循环来找根节点
nextRoot = head;
return NULL;
}
int ln = n>>1 ,rn = n-1-ln;
TreeNode *left = turn(head, nextRoot, ln); //将左子树转为平衡二叉树后,nextRoot会指向当前子树的根节点
TreeNode *root = nextRoot;
TreeNode *right = turn(nextRoot->right, nextRoot, rn); //将右子树转为平衡二叉树后,nextRoot会指向当下一次要转换的子树的根节点
root->left = left;
root->right = right;
return root;
}
};
作者:aninvalidname 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/balance-a-binary-search-tree/solution/c-xian-zhuan-wei-lian-biao-zai-di-gui-zhuan-wei-yi/
其他
Leetcode-117.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
本题如果使用二叉树的层次遍历,在每一层上连接next指针,是比较容易解决的,但是题目进阶的要求是时间复杂度为O(1)。题解中给出了一个符合该要求的方法:
一旦在某层的节点之间建立了 next指针,那这层节点实际上形成了一个链表。因此,如果先去建立某一层的next 指针,再去遍历这一层,就无需再使用队列了。
基于该想法,提出降低空间复杂度的思路:如果第 i 层节点之间已经建立next 指针,就可以通过 next 指针访问该层的所有节点,同时对于每个第 i 层的节点,我们又可以通过它的left 和 right 指针知道其第 i+1 层的孩子节点是什么,所以遍历过程中就能够按顺序为第i+1 层节点建立next 指针。
class Solution {
public:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
Node* ptr = root, *front = root;
while(front != nullptr){
// 确定下一行的起点
front = nullptr;
while(ptr != nullptr && front == nullptr){
if(ptr->left != nullptr) front = ptr->left;
else front = ptr->right;
if(front == nullptr) ptr = ptr->next;
}
// 用next来连接下一行
Node * temp = nullptr;
while(ptr != nullptr){
queue<Node*> q;
if(ptr->left != nullptr) q.push(ptr->left);
if(ptr->right != nullptr) q.push(ptr->right);
while(!q.empty()){
if(temp == nullptr) temp = q.front();
else{
temp->next = q.front();
temp = q.front();
}
q.pop();
}
ptr = ptr->next;
}
// 进入下一行
ptr = front;
}
return root;
}
};